Polygon Advances, But Is Rejected At $1.20
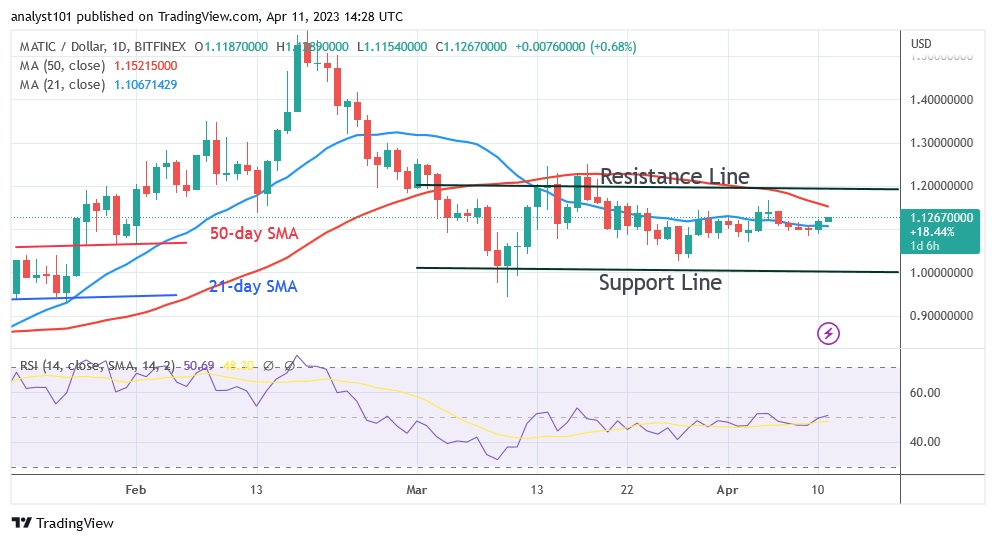
April 11, 2023The price of Polygon (MATIC) has leveled off since its March 9 decline. Currently, the asset is worth between $1 and $1.20 in cryptocurrencies.
Long-term forecast of the price of Polygon: fluctuation range
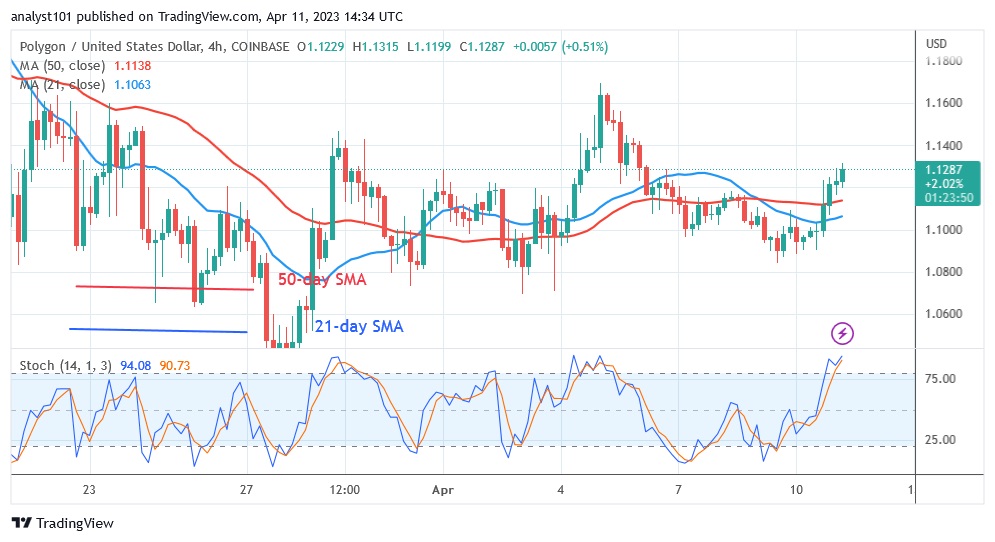
At the time of writing, MATIC is trading for $1.12. Beyond that, the moving average lines are a trap. Polygon is on its way up to retest either the $1.20 resistance level or the 50-day line SMA. The altcoin will rise to a high of $1.56 if the resistance levels are broken. The price will remain in a sideways trend if buyers fail to keep it above the 50-day moving average line. In recent months, the MATIC has been confined to a specific area. Right now, it is trapped between the moving average lines. The altcoin will develop a trend when the moving average lines are broken.
Polygon indicator analysis
For the period 14, Polygon is at 50 on the Relative Strength Index.
The altcoin has reached the equilibrium price level as a result of the recent price movement. This means that supply and demand are now in equilibrium. The price bars have risen between the moving average lines, indicating that the cryptocurrency will continue to move in a range. MATIC is currently trading above the 80 level of the daily stochastic. The altcoin is overbought and may now start to fall.
Technical indicators
Resistance levels: $1.20, $1.30, $1.40
Support levels: $1.00, $0.90, $0.80
What is the next step for Polygon?
Polygon has reached a point where the market is overbought.
As the altcoin approaches the overbought area of the market, the current uptrend could come to an end. MATIC could continue to range as it was likely trapped between the moving average lines.
Disclaimer. This analysis and forecast are the personal opinions of the author and are not a recommendation to buy or sell cryptocurrency and should not be viewed as an endorsement by CoinIdol. Readers should do their own research before investing in funds.
Source: Read Full Article